
Impact of inflation on mutual fund
Before knowing the impact of inflation on mutual funds, we should understand the concept of inflation and mutual funds. Let us first look at the concept of inflation.
What is inflation?
Inflation is nothing but the general rise in prices of goods and services of a nation over a period. In other words, inflation can be defined as the decline of purchasing power of a given currency over time. Inflation rate gives us the percentage increase in the basket of goods and services compared with specific period i.e. base year. Every one of us heard our parents talking about the prices of goods in previous times and how it increased over time. The causes of inflation can be either more demand for goods than what is available in the market causing prices to rise or it could be due to increase in the costs of inputs in production process.
The following are considered as some of the main causes for inflation:
Inflation reduced the purchasing power of the currency: The amount of goods you could buy with ₹ 2000 in 2010 is cheaper that what you can buy in 2020 because purchasing power of India Rupee has fallen due to inflation over time.
For example: Suppose you buy a burger today for ₹ 100 and the yearly inflation is 6%. This means that next year you would need ₹ 106 to buy the same burger. You see, how the purchasing power of ₹ 100 decreased due to inflation. If your income next year would not increase as per inflation, then it is possible that you will not be able to buy that burger next year.
There are two indexes in India which gives us the numerical figure of inflation and these two are Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Wholesale price Index (WPI).
Wholesale Price Index (WPI): This index shows the changes in the wholesale prices. It does not include the fluctuations of price in the retail market and services sector.
Consumer Price Index (CPI): This index gives the price changes of the basket of goods and services at retail level.
As a result of inflation, the value of your money tends to decrease over time. Therefore, you must make sure to align and diversify your investments so that you can generate inflation-proof corpus.
Given below is the chart showing the historic CPI inflation Rate in India since the year 1960
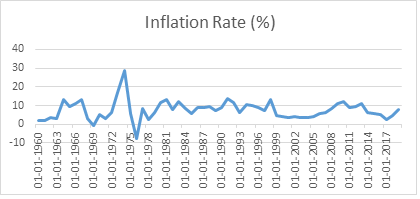
From the graph we can understand that India’s CPI inflation was within the 10% range annually except for the few years. In the year 1974 India recorded its highest CPI inflation due the aftereffects of the 1971 war and the OPEC slashed the production and increased the crude oil prices by a whopping 3x. Since the year 1960 to till now, India’s average annual CPI inflation rate is around 7%.
The following Chart shows how the Rupee value has changed per Dollar historically since the year 2009
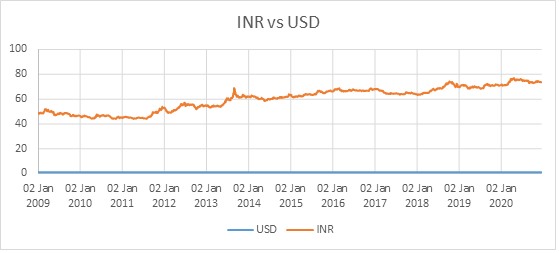
From the graph, we can understand that over the past few years, Indian Rupee has gradually depreciated Vs US dollar. In the year 2009 it was trading in the range of ₹ 48 per US dollar and presently it trades close to ₹ 73 per US dollar. This means, over the years, due to rise in inflation the value of the Indian Rupee has decreased resulting in reduction of the purchasing power of our currency.
What are mutual funds?
Mutual funds pool money from different investors and then use this pooled money to invest in financial markets. The investments of mutual fund houses are managed by experienced professionals who knows the nitty gritty of financial market and invest the money wisely in order to reap maximum gains. They can invest in different assets classes depending upon the theme of funds.
Let us take another example to see how inflation erodes the value of your money. Suppose you have idle cash of ₹ 1, 00,000 at your home today and assume inflation rate to be around 7% p.a.
| Year | Value (in Rupees) |
|---|---|
| 2020 | 1,00,000 |
| 2030 | 50,835 |
| 2040 | 25,842 |
| 2050 | 13,137 |
You can see from the above table that how you’re ₹ 1,00,000 will be of only ₹ 13,137 in 2050 if inflation continues to be at 7%.pa. We could realize from this that instead of keeping it idle at home if we would have invested it then we may be better off in 2050.
Whenever we compare the returns on investments, we should look at real returns because real returns are the returns which you get after subtracting inflation from nominal return. Let us understand the impact of inflation on mutual funds with an example. Suppose there is some person say A who has ₹ 2000 in his hand and he wants to invest it in saving accounts and large cap equity mutual funds. He invested ₹ 1,000 in saving account and ₹ 1,000 in large cap equity mutual funds for a period of 5 years. Inflation in the economy is 6% on an average for 5 years and average saving accounts returns is 4% so after 5 years his returns on savings account would be approximately ₹ 909 after adjusted for inflation. Now, let us look at his returns on large cap equity mutual funds with average large cap returns at 14% for 5 years. He would get ₹ 1438 after adjusting for inflation.
You could see from the above example that how inflation has eaten up your money in savings account, but it still manages to give you more in large cap equity mutual funds.
How to beat inflation with a portfolio of mutual funds?
Building a portfolio of mutual funds is like building a house. To build the best portfolio of mutual funds, one must go beyond the wise advice, “Do not put all your eggs in one basket.”. A structure that will stand the test of time requires a smart design, a strong foundation and simple combination of the mutual funds that will work well for your needs. Make sure that you have a diversified portfolio, means, you have exposure to the different categories of mutual funds. Historically equity mutual funds have shown to generate returns which beat the inflation and therefore it is an important ingredient of your portfolio.
Given below is a sample portfolio for aggressive investors who are ready to take high risks for higher returns and returns have beaten the inflation by a huge margin:
| Scheme | 5 Year Returns |
|---|---|
| Axis Bluechip Fund | 15.09% |
| Canara Robeco Equity Diversified Fund | 13.32% |
| Invesco India Multicap Fund | 10.12% |
| Parag Parikh Long Term Equity Fund | 15.09% |
| SBI Focused Equity Fund | 12.65% |
One can make portfolio of moderate equity portfolio also and still manage to get returns to beat the inflation.
Conclusion: In order to contain the crippling effect of inflation, it is important that you invest in equity-oriented mutual funds as these funds give higher returns than the inflation and therefore one’s wealth is appreciated instead of reduction or eaten up by the growing inflation. It is also advisable to balance the portfolio with adequate debt mutual funds to get less volatility of returns.

