Mutual Fund
Trust that pools the savings of a number of investors who share a common financial goal.Structure of Mutual Fund
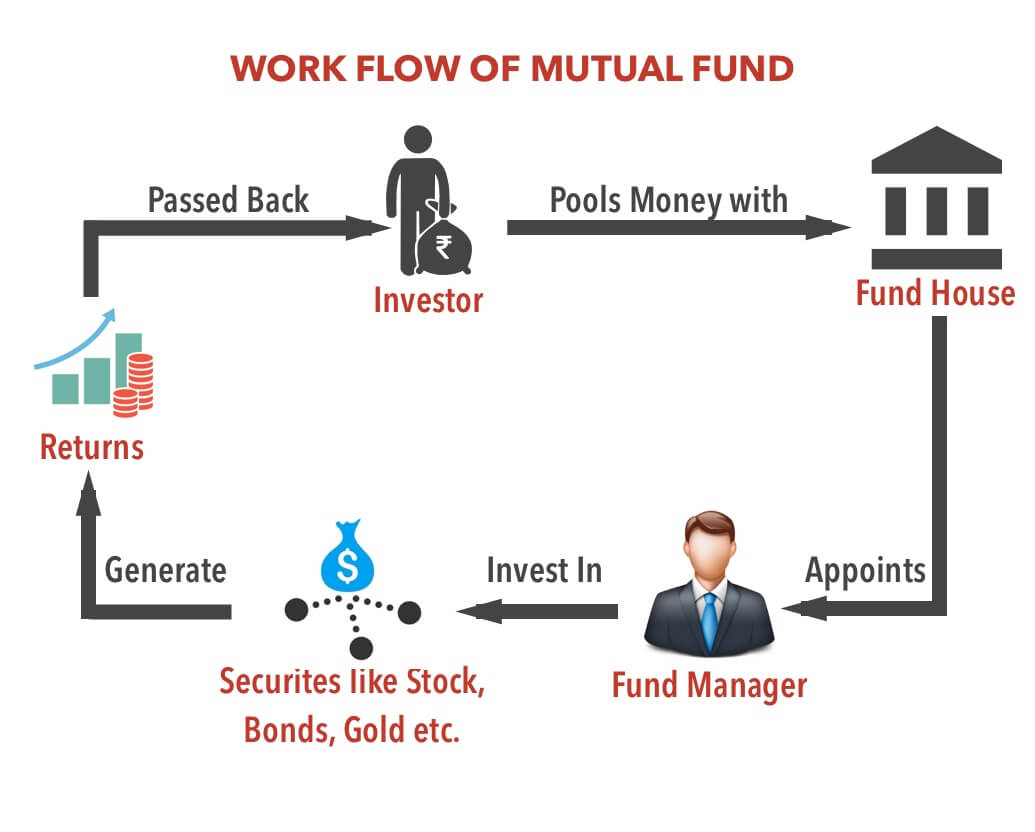
Mutual fund is an investment product that trades in diversified holdings like stocks, bonds, gold, real estate etc. with a long term investment objective, mutual funds are professionally managed by fund managers, who have access to the right research, market information and methodology to make sound investment decisions. We at SIPfund.com offer you the best mutual funds possible after a comprehensive review of the portfolio.
Mutual Fund
A mutual fund is a trust that pools the savings of a number of investors who share a common financial goal.
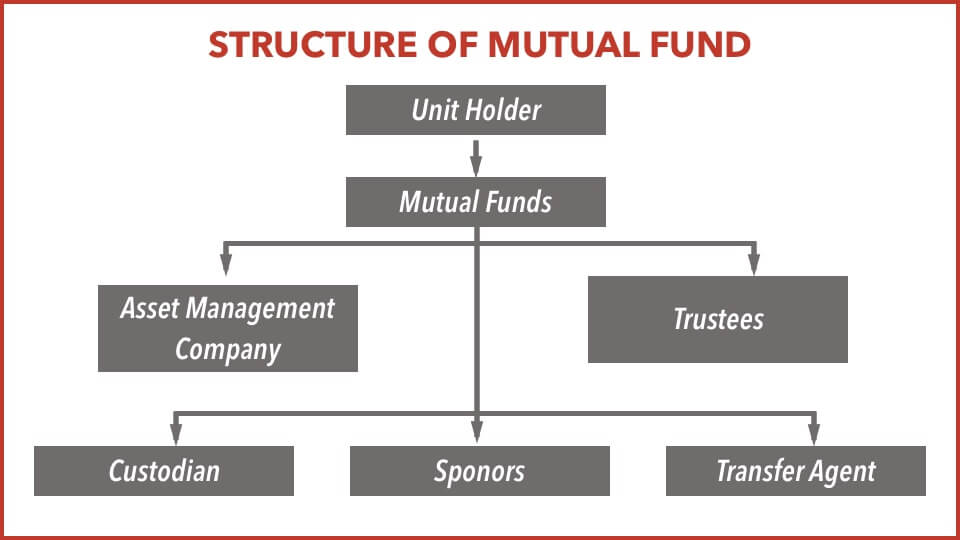
Unit Holders: Investor
Mutual Fund Scheme: A particular Scheme with a predefined investment objective
Asset Management Company (AMC): A company that invests its clients' pooled fund into securities that match its declared financial objectives.
Trustees: The Trustees shall ensure that the AMC has put in place adequate back office, dealing and accounting systems. The Trustees shall ensure that the AMC has appointed all key personnel, including fund manager(s) for the various schemes, auditors, compliance officers, registrars, etc. The Trustee should also ensure preparation of the compliance manual and design internal control mechanisms, including internal audit systems.
Custodian: Keeps safe custody of the investment related documents of securities invested.
Sponsors: A Sponsor establishes the Mutual Fund along with any individual/body corporate. The Sponsor’s liability is restricted to his contribution. Sponsor must contribute a minimum 40% to the net worth of AMC. Sponsor is a person who has a continuing interest in the Mutual Fund and whose credibility is significantly responsible for mobilizing the savings of the public for the Mutual Fund.
Transfer Agents: Registrar or transfer agents are the trusts or institutions that register and maintain detailed records of the transactions of investors for the convenience of mutual fund houses.
Types of Mutual Fund
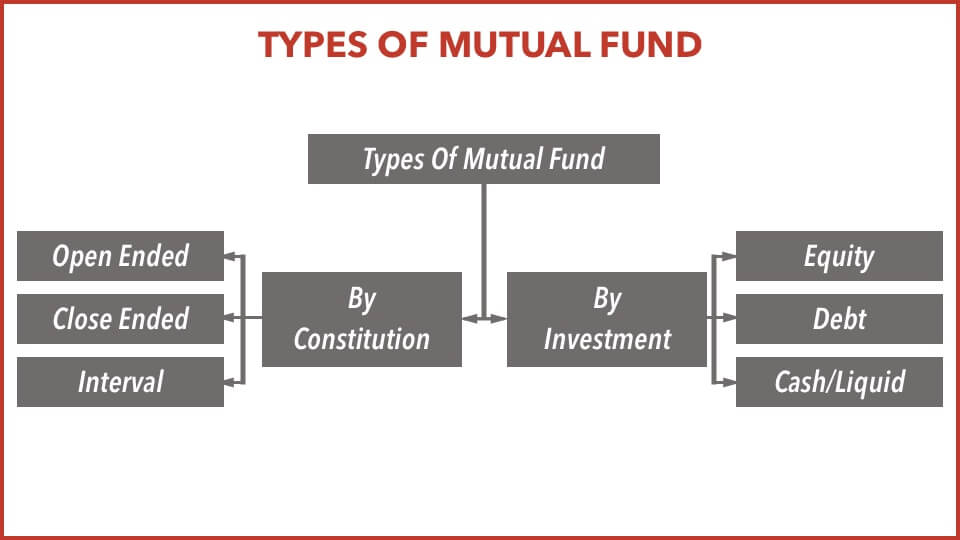
Types of Mutual Fund by Constitution
Open Ended Funds: These funds buy and sell units on a continuous basis and allow investors to enter and exit the fund according to their convenience. The units can be purchased and sold even after the initial offering (NFO) period (in case of new funds).
Closed Ended Funds: A closed-end fund is an investment fund that raises a fixed amount of capital through an NEW FUND OFFER (NFO). Close ended funds invest with a predefined investment objective of type of securities to be held in the portfolio along with a pre-defined maturity date.
- After NFO Period, further investments are restricted with in the fund.
- The fund is then structured, listed and traded like a stock on a stock exchange
Interval Funds: A fund that combines the features of open-ended and closed-ended schemes, the fund is open for sale or redemption during pre-determined intervals.
Types of Mutual Fund by Underlying Investment
Equity Funds: The fund managers of equity fund invest in equities with predefined investment theme. For example a large cap equity scheme means the underlying equity stocks are large cap equity stocks. The Fund managers take active role in studying the company before investing and also keep a close watch on the performance of the company. They are guided and regulated by SEBI for their actions in investments.
Fund managers are expected to take adequate measures to safeguard the interest of the investor by diversification and active management of the equities.
Debt Funds: A debt mutual fund is similar to borrowing and lending. Mutual fund lends to the borrower after due consideration to following laid down conditions;
- Reasonable assurance that the principal investment will be returned.
- The interest that will be generated based on the rate of interest (also known as the coupon rate).
- Tenure or the time over which the principal will be returned.
Companies, state governments and even the central government all require money to run their operations. They offer various debt based instruments like T-Bills, Debentures, and G-Secs etc. Mutual Funds buy the debt that is issued by them. These Funds would typically invest in government securities, NCD, CDs, CPs bonds and other fixed income securities as well as lend money to large organizations or Corporates, in return of a fixed interest rate.
Cash or Liquid Funds: In financial terms, the word Liquid simply means cash.
A highly liquid asset is as good as hard cash.
- Liquid Mutual Funds have the least risk factor and may give you returns that are slightly higher than a savings account.
- These funds invest in faster maturing debt securities, therefore making them less risky.
- The closer the debt instrument is to its maturity, the higher the chances and surety of you getting the principal and interest.
Other types of mutual funds
Hybrid Fund: A category of mutual fund that is characterized by portfolio that is made up of a mix of stocks and bonds, which can vary proportionally over time or remain fixed.
Sector Fund: 'Sector Fund' a stock mutual, exchange-traded or closed-end fund that invests solely in businesses that operate in a particular industry or sector of the economy.
Thematic Fund: They have a broader spectrum when compared to sector funds, but is limited when compared to Diversified equity mutual funds. Thematic funds by nature are more prone to risk and volatility.
Advantages of Mutual Funds:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Professional Management
Diversification
Convenient Administration
Return potential
Low cost
Liquidity
Transparency
Flexibility
Choice of schemes
Well regulated
Tax benefits
NAV (Net Asset Value)
The value of all the securities in mutual funds portfolio is calculated on daily basis. From this, all expenses are deducted and the resultant value divided by the number of units in the fund is the funds NAV or its Net Asset Value.

WORK FLOW OF MUTUAL FUND